With last week’s revelation that the EU Digital Markets Act
will require tech gatekeepers (companies valued at over $75B or with over
$7.5B of turnover) to open their communication APIs for the purposes of
interoperability, there’s been a lot of speculation on what this could mean
in practice, To try to ground the conversation a bit, we’ve had a go at
outlining some concrete proposals for how it could work.
However, before we jump in, we should review how the DMA has come to pass.
🔗What’s driven the DMA?
Today’s gatekeepers all began with a great product, which got more and more
popular until it grew to such a size that one of the biggest reasons to use
the service is not necessarily the product any more, but the benefits of
being able to talk to a large network of users. This rapidly becomes
anti-competitive, however: the user becomes locked into the network and can’t
switch even if they want to. Even when people have a really good reason
to move provider (e.g. WhatsApp’s terms of use changing to
share user data with Facebook, Apple doing a 180 on end-to-end encrypting iCloud backups,
or Telegram not actually being end-to-end encrypted),
in practice hardly anything changes -
because the users are socially obligated to keep using the service in order
to talk to the rest of the users on it.
As a result, it’s literally harmful to the users. Even if a new service
launches with a shiny new feature, there is enormous inertia that must be
overcome for users to switch, thanks to the pull of their existing network -
and even if they do, they’ll just end up with their conversations haphazardly
fragmented over multiple apps. This isn’t accepted for email; it isn’t
accepted for the phone network; it isn’t accepted on the Internet itself -
and it shouldn’t be accepted for messaging apps either.
Similarly: the closed networks of today’s gatekeepers put a completely
arbitrary limit on how users can extend and enrich their own conversations.
On email, if you want to use a fancy new client like Superhuman - you can. If
you want to hook up a digital assistant or translation service to help you
wrangle your email - you can. If you want to hook up your emails to a CRM to
help you run your business - you can. But with today’s gatekeepers, you have
literally no control: you’re completely at the mercy of the service
provider - and for something like WhatsApp or iMessage the options are
limited at best.
Finally - all the users’ conversation metadata for that service (who talks to
who, and when) ends up centralised in the gatekeepers’ databases, which then
become an incredibly valuable and sensitive treasure trove, at risk of abuse.
And if the service provider identifies users by phone number, the user is
forced to disclose their phone number (a deeply sensitive personal
identifier) to participate, whether they want to or not. Meanwhile the user
is massively incentivised not to move away: effectively they are held hostage
by the pull of the service’s network of users.
So, the DMA exists as a strategy to improve the situation for users and
service providers alike by building a healthier dynamic ecosystem for
communication apps; encouraging products to win by producing the best quality
product rather than the biggest network. To quote Cédric O (Secretary of
State for the Digital Sector of France), the strategy of the legislation came
from Washington advice to address the anticompetitive behaviour of the
gatekeepers “not by breaking them up… but by breaking them open.” By
requiring the gatekeepers to open their APIs, the door has at last been
opened to give users the option to pick whatever service they prefer to use,
to choose who they trust with their data and control their conversations as
they wish - without losing the ability to talk to their wider audience.
However, something as groundbreaking as this is never going to be completely
straightforward. Of course while some basic use cases (i.e. non-E2EE chat)
are easy to implement, they initially may not have a UX as smooth as a closed
network which has ingested all your address book; and other use cases(eg E2EE
support) may require some compromises at first. It’s up to the industry to
figure out how to make the most of that challenge, and how to do it in a way
which minimises the impact on privacy - especially for end-to-end encrypted
services.
🔗What problems need to be solved?
We’ve already written about this
from a Matrix perspective, but to recap - the main challenge is the trade-off
between interoperability and privacy for gatekeepers who provide end-to-end
encryption, which at a rough estimate means: WhatsApp, iMessage, secret chats
in Facebook Messenger, and Google Messages. The problem is that even with
open APIs which correctly expose the end-to-end encrypted semantics (as DMA
requires), the point where you interoperate with a different system
inevitably means that you’ll have to re-encrypt the messages for that system,
unless they speak precisely the same protocol - and by definition you end up
trusting the different system to keep the messages safe. Therefore this
increases the attack surface on the conversations, putting the end-to-end
encryption at risk.
Alex Stamos (ex-CISO at Facebook) said that “WhatsApp rolling out mandatory
end-to-end encryption was the largest improvement in communications privacy
in human history” – and we agree.
Guaranteed end-to-end encrypted conversations on WhatsApp is amazing, and
should be protected at all costs. If users are talking to other users on
WhatsApp (or any set of users communicating within the same E2EE messenger),
E2EE should and must be maintained - and there is nothing in the DMA which says otherwise.
But what if the user consciously wants to prioritise interoperability over
encryption? What if the user wants to hook their WhatsApp messages into a
CRM, or run them through a machine translation service, or try to start a
migration to an alternative service because they don’t trust Meta? Should
privacy really come so spectacularly at the expense of user freedom?
We also have the problem of figuring out how to reference users on other
platforms. Say that I want to talk to a user with a given phone number, but
they’re not on my platform - how do I locate them? What if my platform only
knows about phone numbers, but you’re trying to talk to a user on a platform
which uses a different format for identifiers?
Finally, we have the problem of mitigating abuse: opening up APIs makes it
easier for bad actors to try to spam or phish or otherwise abuse users within
the gatekeepers. There are going to have to be changes in anti-abuse
services/software, and some signals that the gatekeeper platforms currently
use are going to go away or be less useful, but that doesn't mean the whole
thing is intractable. It will require changes and innovative thinking, but
we’ve been making steady progress (e.g. the work done by Element’s trust and
safety team). Meanwhile, the
gatekeepers already have massive anti-abuse systems in place to handle the
billions of users within their walled gardens, and unofficial APIs are
already widespread: adding official APIs does not change the landscape
significantly (assuming interoperability is implemented in such a way that
the existing anti-abuse mechanisms still apply).
In the past, gatekeepers dismissed the effort of interop as not being
worthwhile - after all, the default course of action is to build a walled
garden, and having built one, the temptation is to try to trap as many users
as possible. It was also not always clear that there were services worth
interoperating with (thanks to the chilling effects of the gatekeepers
themselves, in terms of stifling innovation for communication startups).
Nowadays this situation has fundamentally changed however: there is a vibrant
ecosystem of open communication startups out there, and a huge appetite to
build a vibrant open ecosystem for interoperable communication, but like the
open web itself.
🔗What are the requirements?
Before going further in considering solutions, we need to review the actual
requirements of the DMA. Our best understanding at this point is that the
DMA will mandate that:
- Gatekeepers will have to provide open and documented APIs to their services, on request, in order to facilitate interoperability (i.e. so that other services can communicate with their users).
- These APIs must preserve the same level of end-to-end encryption (if any) to remote users as is available to local users.
- This applies to 1:1 messaging and file transfer in the short term, and group messaging, file-transfer, 1:1 VoIP and group VoIP in the longer term.
🔗So, what could this actually look like?
The DMA legislation deliberately doesn’t focus on implementation, instead
letting the industry figure out how this could actually work in practice.
There are many different possible approaches, and so from our point of view
as Matrix we’ve tried to sketch out some options to make the discussion more
concrete. Please note these are preliminary thoughts, and are far from
perfect - but hopefully useful as a starting point for discussion.
🔗Finding Bob
Imagine that you have a user Alice on an existing gatekeeper, which we’ll call
AliceChat, who runs an E2EE messaging service which identifies users using
phone numbers. Say that they want to start a 1-to-1 conversation with Bob,
who doesn’t use AliceChat, but Alice knows he is a keen user of BobChat.
Today, you’d have no choice but to send them an SMS and nag them to join
AliceChat (sucks to be them if they don’t want to use that service, or if
they’re unable to for whatever reason - e.g. their platform isn’t supported,
or their government has blocked access, etc), or join BobChat yourself.
However, imagine if instead the gatekeeper app had a user experience where the
app prompted you to talk to the user via a different platform instead. It’d
be no different to your operating system prompting you to pick which app to
use to open a given file extension (rather than the OS vendor hardcoding it
to one of their own apps - another win for user rights led by the EU!).
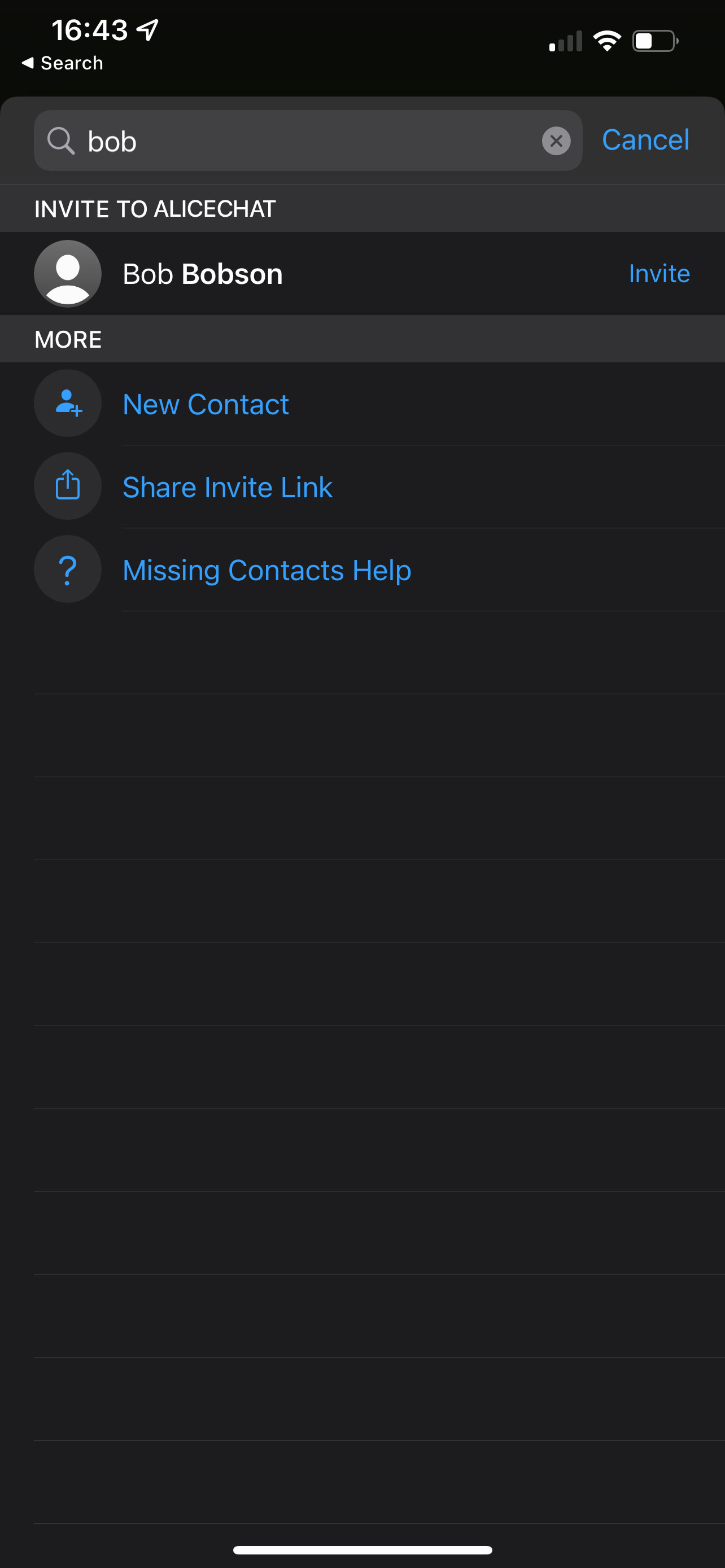
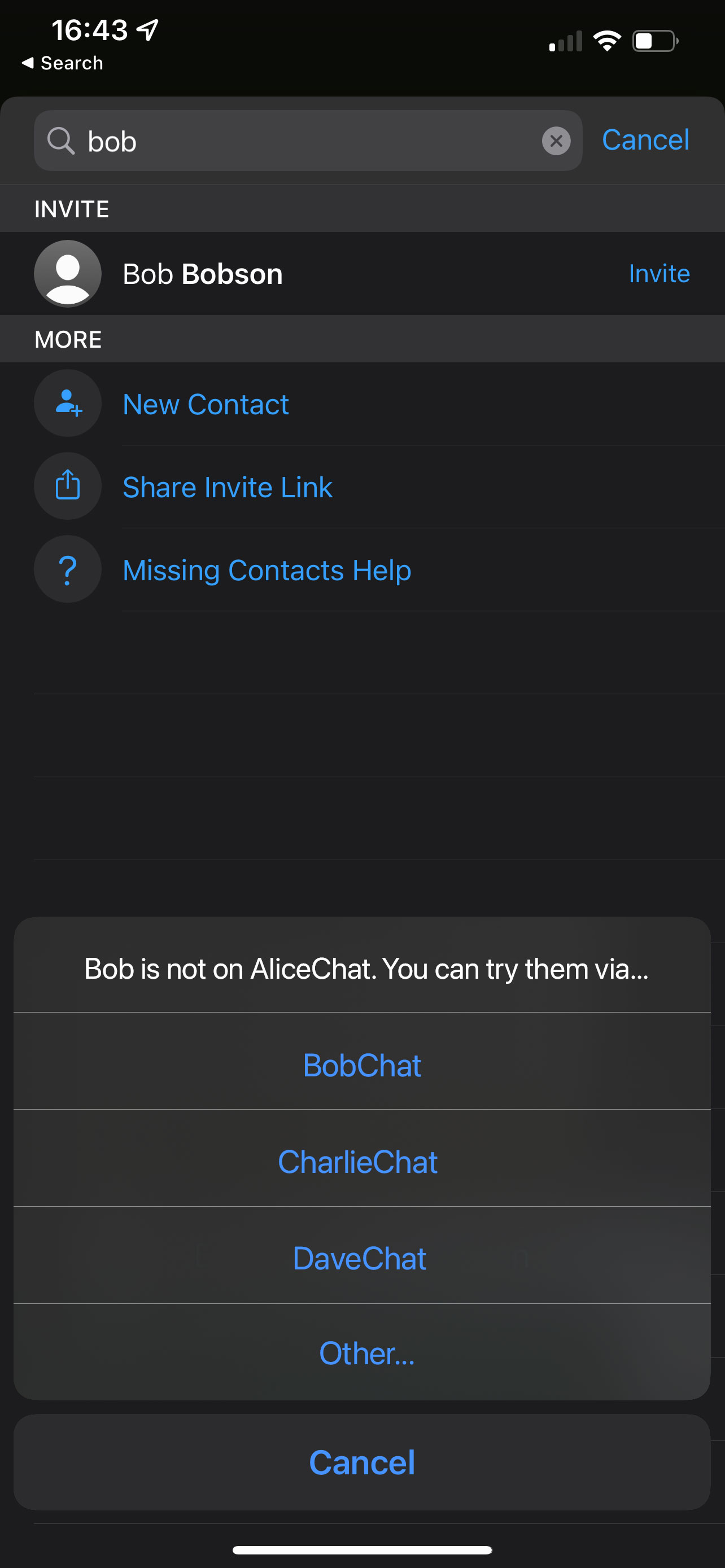
Now, the simplest approach in the short term would be for each gatekeeper to
pre-provision a set of options of possible alternative networks. (The DMA
says that, on request, other service providers can ask to have access to the
gatekeeper’s APIs for the purposes of interoperability, so the gatekeeper
knows who the alternative networks may be). “Bob is not on AliceChat - do
you want to try to reach him instead on BobChat, CharlieChat, DaveChat
(etc)”.
Much like users can configure their preferred applications for file extensions
in an operating system today, users would also be able to add their own
preferred service providers - simply specifying their domain name.
🔗Connecting to Bob
Now, AliceChat itself needs to figure out how to query the remote service
provider to see if Bob actually exists there. Given the DMA requires that
gatekeepers provide open APIs with the same level of security to remote users
as their local ones using today’s private APIs - and very deliberately
doesn’t mandate specific protocols for interoperability - they will need to
locate a bridge which can connect to the other system.
In this thought experiment, the bridge used would be up to the destination
provider. For instance, bobchat.com could announce that AliceChat users
should connect to it via alicechat-bridge.bobchat.com using the AliceChat
protocol(or matrix-bridge.bobchat.com via Matrix or xmpp-bridge.bobchat.com
via XMPP) by a simple HTTP API or even a .well-known URL. Users might also
be able to override the bridge used to connect to them (e.g. to point instead
at a client-side bridge), and could sign the advertisement to prove that it
hadn’t been tampered with.
AliceChat would then connect to the discovered bridge using AliceChat’s
vendor-specific newly opened API, and would then effectively treat Bob as if
they were a real AliceChat user and client to all intents and purposes. In
other words, Bob would effectively be a “ghost user” on AliceChat, and
subject to all their existing anti-abuse mechanisms.
Meanwhile, the other side of the bridge converts through to whatever the
target system is - be that XMPP, Matrix, a different proprietary API, etc.
For Matrix, it’d be chatting away to a homeserver via the Application Service
API (using
End-to-Bridge Encryption via
MSC3202).
It’s also worth noting that the target might not even be a bridge - it could
be a system which already natively speaks AliceChat’s end-to-end encrypted
API, thus preserving end-to-end encryption without any need to re-encrypt.
It’s also worth noting that while historically bridges have had a bad
reputation as being a second class (often a second class afterthought),
Matrix has shown that by considering them as a first class citizen and really
focusing on mapping the highest common denominator between services rather
than lowest common denominator, it’s possible for them to work transparently
in practice. Beeper is a great example of Matrix
bridging being used for real in the wild (rather amusingly they just
shipped emoji reactions for WhatsApp on iOS via their
WhatsApp<->Matrix bridge before WhatsApp themselves did…)
Architecturally, it could look like this:
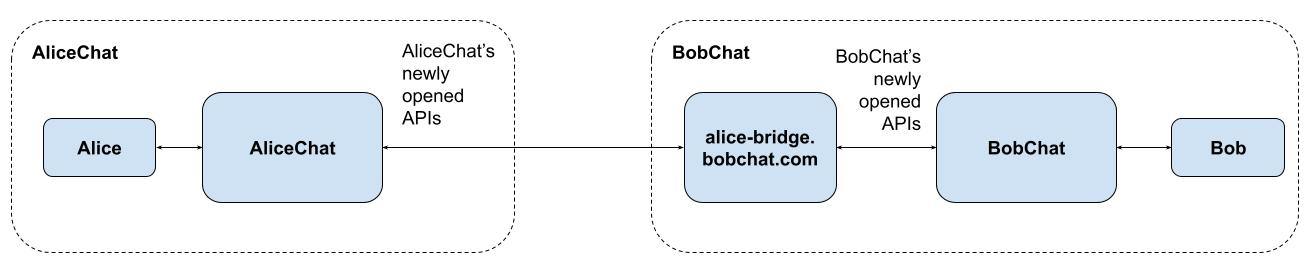
Or, more likely (given a dedicated bridge between two proprietary services
would be a bit of a special case, and you’d have to solve the dilemma of who
hosts the bridge), both services could run a bridge to a common open standard
protocol like Matrix or XMPP instead (thus immediately enabling
interoperability with everyone else connected to that network):
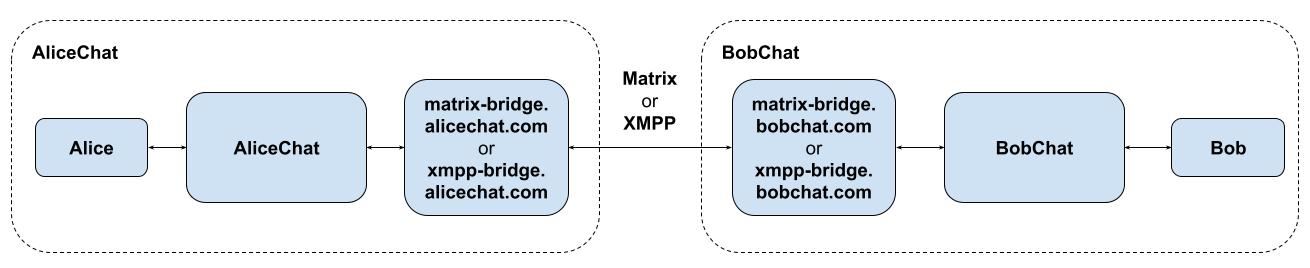
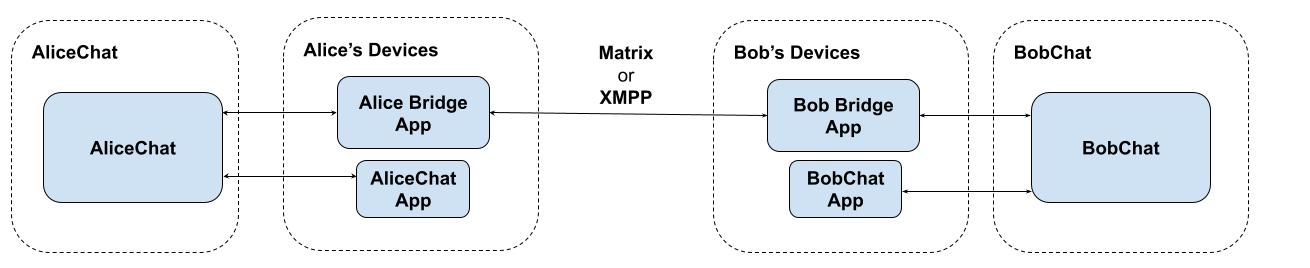
Please note that while these examples show server-side bridges, in practice it
would be infinitely preferable to use client-side bridges when connecting to
E2EE services - meaning that decrypted message data would only ever be
exposed on the client (which obviously has access to the decrypted data
already). Client-side bridges are currently complicated by OS limits on
background tasks and push notification semantics (on mobile, at least), but
one could envisage a scenario where you install a little stub AliceChat
client on your phone which auths you with AliceChat and then sits in the
background receiving messages and bridging them through to Matrix or XMPP,
like this:
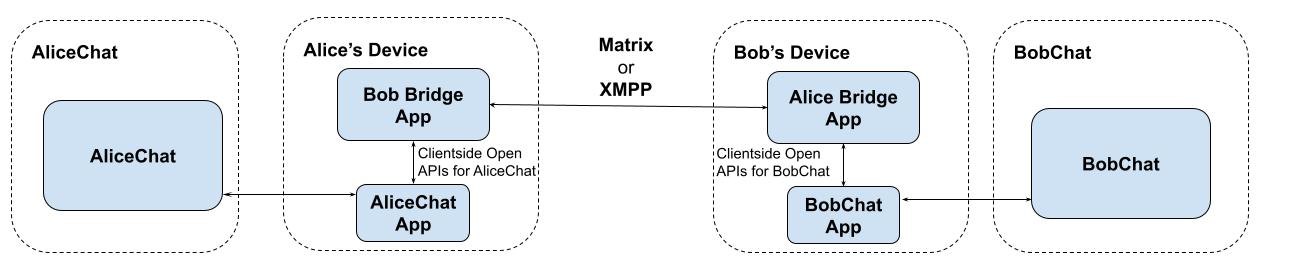
Another possible architecture could be for the E2EE gatekeeper to expose their
open APIs on the clients, rather than the server. DMA allows this, to the
best of our knowledge - and would allow other apps on the device to access
the message data locally (with appropriate authorisation, of course) - effectively
doing a form of realtime
data liberation
from the closed service to an open system, looking something like this:
Finally, it's worth noting that when peer-to-peer decentralised protocols
like P2P Matrix
enter production, clientside bridges could bridge directly into a local
communication server running on the handset - thus avoiding metadata being
exposed on Matrix or XMPP servers providing a common language between the
service providers.
🔗Locating users
Now, the above describes the simplest and most naive directory lookup system
imaginable - the problem of deciding which provider to use to connect to each
user is shouldered by the users. This isn’t that unreasonable - after all,
users may have strong feelings about what providers to use to talk to a given
user. Alice might be quite happy to talk to Bob via BobChat, but might be
very deliberately avoiding talking to him on DaveChat, for whatever ominous
reasons.
However, it’s likely in future we will also see other directory services
appear in order to map phone numbers (or other identities) to providers -
whether these piggyback on top of existing identity providers
(gatekeepers, DNS, telcos, SSO providers, governments) or are decentralised
through some other mechanism. For instance, Bob could send AliceChat a
blinded proof that he authorises them to automatically route traffic to him
over at BobChat, with BobChat maintaining a matching proof that Bob is who he
claims to be (having gone through BobChat’s auth process) - and the proofs
could be linked using a temporary key such that Bob doesn’t even need to
maintain a long-term one. (Thanks to James Monaghan for suggesting this one!)
Another alternative to having the user decide where to find each other could
be to use a decentralised Keybase-style identity system to track verified
mappings of identities (phone numbers, email addresses etc) through to
service providers - perhaps something like IDX might fit
the bill? While this decentralised identity lookups have historically been a
hard problem, there is a lot of promising work happening in this space
currently and the future looks promising.
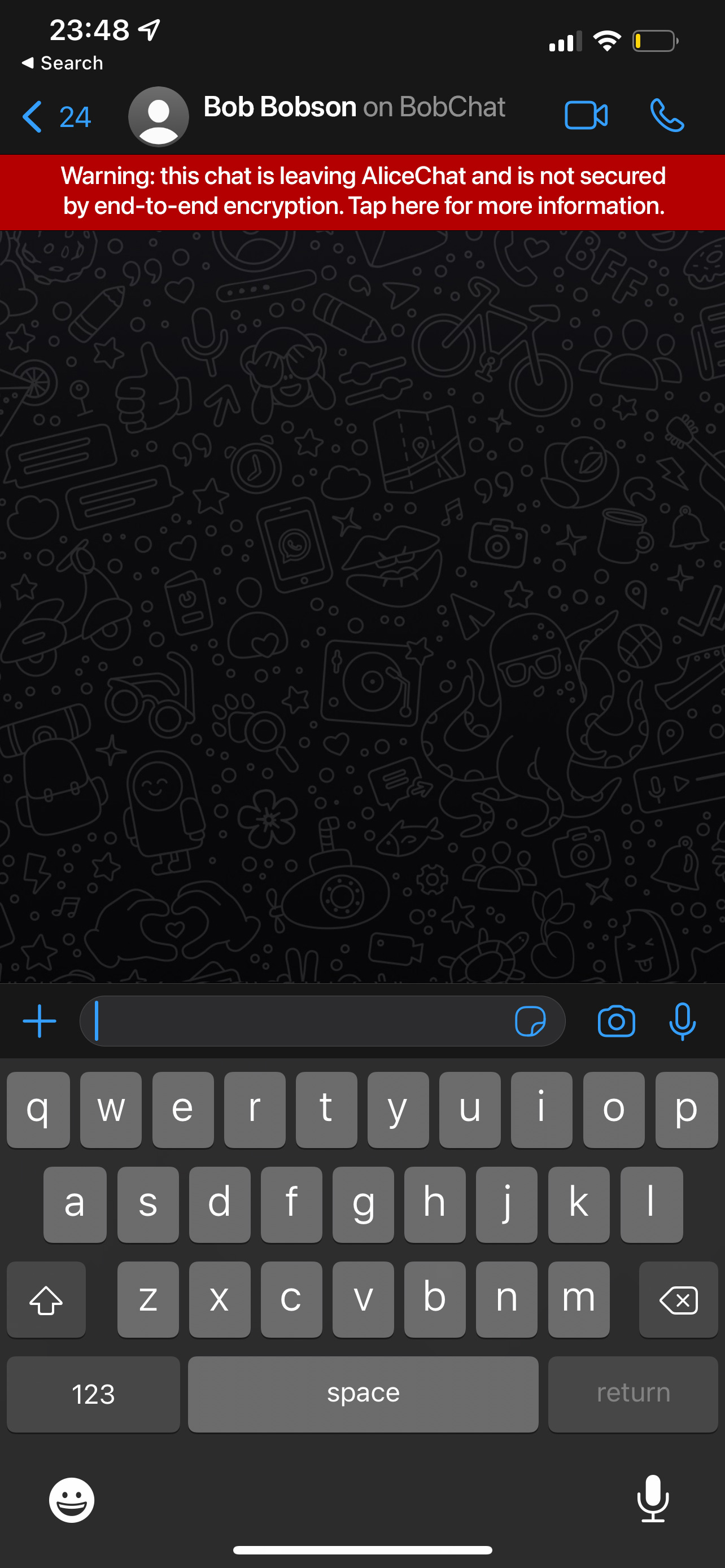
🔗Talking to Bob
Meanwhile, Alice still needs to talk to Bob. As already discussed, unless
everyone speaks the same end-to-end encrypted protocol (be it Matrix,
WhatsApp or anything else), we inevitably have a trade-off here between
interoperability and privacy if Bob is not on the same system as Alice
(assuming AliceChat is end-to-end encrypted) - and we will need to clearly
warn Alice that the conversation is no longer end-to-end encrypted:
To be clear: right now, today, if Bob were on AliceChat, he could be
copy-pasting all your messages into (say) Google Translate in a frantic
effort to workaround the fact that his closed E2EE chat platform has no way
to do machine translation. However, in a DMA world, Bob could legitimately
loop a translation bot into the conversation… and Alice would be warned that
the conversation was no longer secure (given the data is now being bridged
over to Google).
This is a clear improvement in user experience and transparency. Likewise, if
I’m talking to a bridged user today on one of these platforms, I have no way
of telling that they have chosen to prioritise interop over E2EE - which is
frankly terrifying. If I’m talking to someone on WhatsApp today I blindly
assume that they are E2EE as they are on the same platform - and if they’re
using an unofficial app or bridge, I have no way to tell. Whereas in a DMA
world, you would expect the gatekeeper to transparently expose it.
If anything, this is good news for the gatekeeper in that it consciously
advertises a big selling point for them: that for full E2EE, users need to
talk to other users in the same walled garden (unless of course the platform
speaks the same protocol). No more need for bus shelter adverts to remind
everywhere that WhatsApp is E2EE - instead they can remind the user every
time they talk to someone outside the walled garden!
Just to spell it out: the DMA does not require or encourage any reduction in
end-to-end encryption for WhatsApp or similar: full end-to-end encryption
will still be there for users in the same platform, including through to
users on custom clients (assuming the gatekeeper doesn’t flex and turn it off
for other reasons).
Obviously, this flow only considers the simple case of Alice inviting Bob. The
flow is of course symmetrical for Bob inviting Alice; AliceChat will need to
advertise bridges which can be used to connect to its users. As Bob pops up
from BobChat, the bridge would use AliceChat’s newly open APIs to provision a
user for him, authing him as per any other user (thus ensuring that AliceChat
doesn’t need to have trusted BobChat to have authenticated the user). The
bridge then sends/receives messages on Bob’s behalf within AliceChat.
🔗Group communication
This is all very well for 1:1 chats - which are the initial scope of the DMA.
However, over the coming years, we expect group chats to also be in scope.
The good news is that the same general architecture works for group chats
too. We need a better source of identity though: AliceChat can’t possibly
independently authenticate all the new users which might be joining via group
conversations on other servers (especially if they join indirectly via
another server). This means adopting one of the decentralised identity
lookup approaches outlined earlier to determine whether Charlie on
CharlieChat is the real Charlie or an imposter.
Another problem which emerges with group chats which span multiple service
providers is that of indirect routing, especially if the links between the
providers use different protocols. What if AliceChat has a direct bridge to
BobChat (a bit like AIM and ICQ both spoke OSCAR), BobChat and CharlieChat
are connected by Matrix bridges, and AliceChat and CharlieChat are connected
via XMPP bridges? We need a way for the bridges to decide who forwards
traffic for each network, and who bridges the users for which network. If
they were all on Matrix or XMPP this would happen automatically, but with
mixed protocols we’d probably have to extend the lookup protocol to establish
a spanning tree for each conversation to prevent forwarding loops.
Here’s a deliberately twisty example to illustrate the above thought experiment:
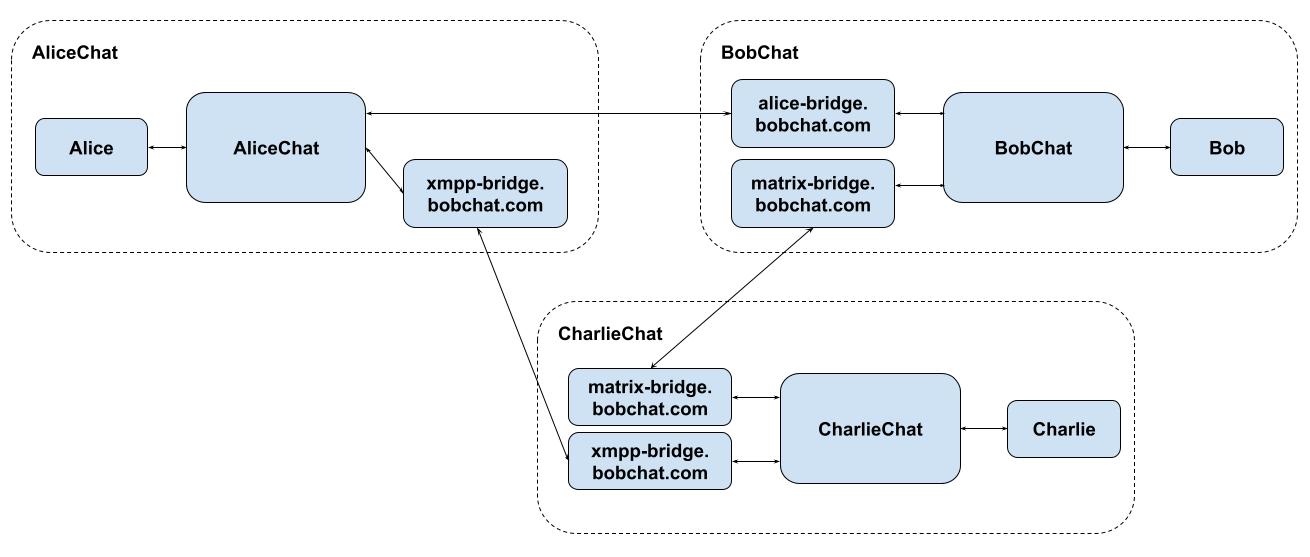
There is also a risk of bridge proliferation here - in the worst case, every
service would have to source bridges to directly connect to every other
service who came along, creating a nightmarish n-by-m problem. But in
practice, we expect direct proprietary-to-proprietary bridges to be rare:
instead, we already have open standard communication protocols like Matrix
and XMPP which provide a common language between bridges - so in practice,
you could just end up in a world where each service has to find a
them-to-Matrix or them-to-XMPP bridge (which could be run by them, or
whatever trusted party they delegate to).
🔗Conclusion
A mesh of bridges which connect together the open APIs of proprietary vendors
by converting them into open standards may seem unwieldy at first - but it’s
precisely the sort of ductwork which links both phone networks and the
Internet together in practice. As long as the bridging provides for highest
common denominator fidelity at the best impedance ratio, then it’s
conceptually no different to converting circuit switched phone calls to VoIP,
or wired to wireless Ethernet, or any of the other bridges which we take
entirely for granted in our lives thanks to their transparency.
Meanwhile, while this means a bit more user interface in the communication
apps in order to select networks and warn about trustedness, the benefits to
users are enormous as they put the user squarely back in control of their
conversations. And the UX will improve as the tech evolves.
The bottom line is, we should not be scared of interoperability, just because
we’ve grown used to a broken world where nothing can interconnect. There are
tractable ways to solve it in a way that empowers and informs the user - and
the DMA has now given the industry the opportunity to demonstrate that it can
work.